The Rosetta spacecraft is capturing ever more breathtaking views of its target comet that are significantly advancing landing site selection for the history making touchdown on the bizarre worlds nucleus by the attached Philae lander.
Today ESA released the latest high resolution images of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko taken by the OSIRIS science camera on Sept. 5, and is shown above.
Jagged cliffs and prominent boulders are clearly visible in unprecedented detail on the head and body of Comet 67P displaying a multitude of different terrains in the new image taken from a distance of 62 kilometers.
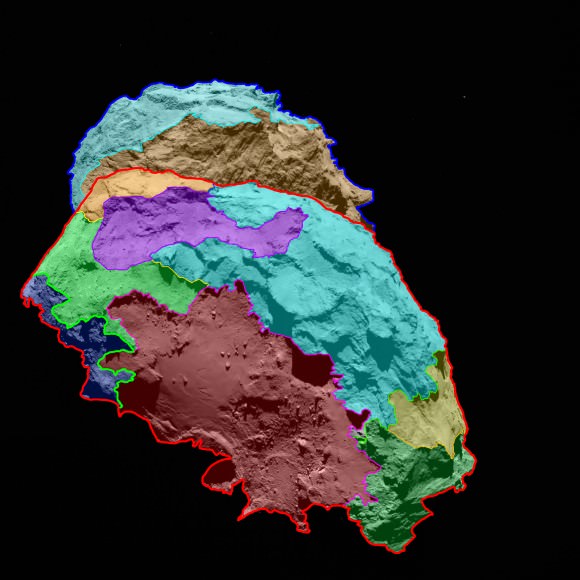
Meanwhile the Rosetta science team is using the OSIRIS and navcam camera images to create a preliminary map of the comets surface. The map is color coded to divide the comet into several distinct morphological regions.
Credits: ESA/Rosetta/MPS for OSIRIS Team MPS/UPD/LAM/IAA/SSO/INTA/UPM/DASP/IDA
“With various areas dominated by cliffs, depressions, craters, boulders or even parallel grooves, 67P/C-G displays a multitude of different terrains. Some areas even appear to have been shaped by the comet’s activity,” the Rosetta team said in the release.
The images were also shown at today’s scientific presentations at a special Rosetta research session at the 2014 European Planetary Science Congress being held in Cascais, Portugal.
The scientists are striving to meld all the imagery and data gathered from Rosetta’s 11 instruments in order to elucidate the composition and evolution of the different regions.
The mapping data is also being used to narrow the ‘Top 5’ Philae landing site candidates down to a primary and backup choice.
The final landing site selections will be made at a meeting being held this weekend on 13 and 14 September 2014 between the Rosetta Lander Team and the Rosetta orbiter team at CNES in Toulouse, France.

Credits: ESA/Rosetta/NAVCAM/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
Philae’s history making landing on comet 67P is currently scheduled for around Nov. 11, 2014, and will be entirely automatic. The 100 kg lander is equipped with 10 science instruments.
The three-legged lander will fire two harpoons and use ice screws to anchor itself to the 4 kilometer (2.5 mile) wide comet’s surface. Philae will collect stereo and panoramic images and also drill 23 centimeters into and sample its incredibly varied surface.
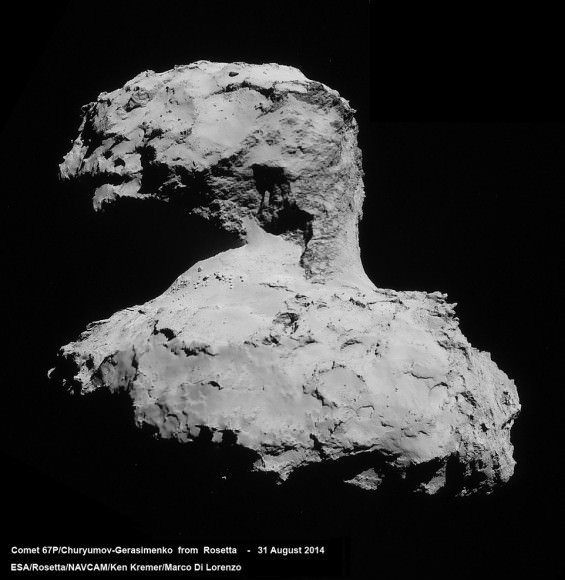

The comet nucleus is about 4 km (2.5 mi) across.
The team is in a race against time to select a suitable landing zone soon since the comet warms up and the surface becomes ever more active as it swings in closer to the sun and makes the landing ever more hazardous.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Rosetta, Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
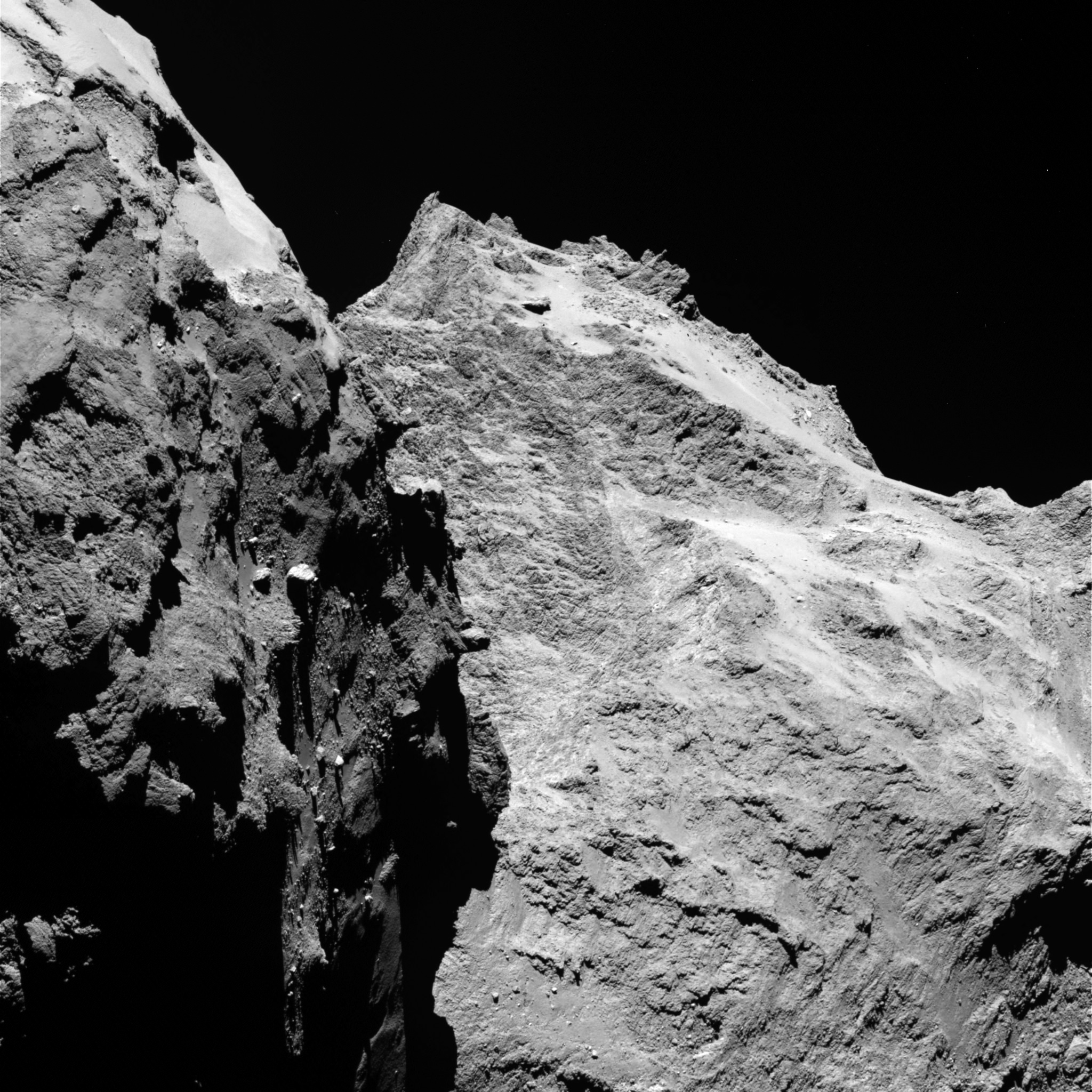



We’re truly living in a Huxleyan “Future Shock” generating science fiction coming true every day kind of world. I mean, first, just look at this world… I mean take a couple minutes and actually ‘see’ it, contemplating the geology/geometry of this thing’s Escherian terrain. In a single shot you have boulders laying on the floor, the 2 different walls and every plane of it’s gambrel roof. Up is a boulder covered surface of a ledge and around the corner is… ANOTHER BOULDERED LEDGE. Gravity is TOTALLY out-of-whack compared to what living on a ginourmous (in comparison) spheroid with a single center thereof leads one to ‘grock’ about it’s nature.
Now take a moment to envision the H.G. Wellsian “HARPOONING” a comet and pulling itself to it’s surface! If THAT isn’t a cover illustration for a pulp science fiction magazine, NOTHING is!
Is our culture so numbed by this unending deluge of “firsts” and “Breakthroughs” in which we reside that the wonder is lost on most, or is it so undereducated that most people are as lost as someone beginning to read Song of Fire and Ice halfway through the fourth book? Or am I so out of touch that I can’t see that there are indeed many, many people as floored as I am every day when I read the science and tech news?
Another GREAT story, Ken!
Dramatic and weird, it looks more interesting than the asteroids we’ve seen up close, like an alpine mountain. A 3d movie flypast would be stunning.
Note to ESA instrument engineers: Put one on your next trip.
I think as far as landing sites are concerned choosing one with a view of the other segment gets my vote. This would show off the gas venting as it heats up.